Cite report
IEA (2020), Clean Household Energy Consumption in Kazakhstan: A Roadmap, IEA, Paris https://www.iea.org/reports/clean-household-energy-consumption-in-kazakhstan-a-roadmap, Licence: CC BY 4.0
Report options
Fuel use in Kazakhstan
Solid fuel use by Kazakh households
The household survey results show that 30% of Kazakhstan’s households used coal and/or firewood in 2018: 17% urban and 55% rural. Survey data demonstrate that household fuel use varies significantly by region due to differences in climate, access to infrastructure and shares of housing types. Thus, solid fuel use differs for urban versus rural dwellers, and for detached houses compared with MABs. In urban areas, 5% of apartments and 46% of detached houses used solid fuels, while in rural areas it was 31% of apartments and 68% of detached houses.
Solid fuels use is more prevalent in regions where district heating and natural gas are unavailable – i.e. the rural areas of northern, central and eastern Kazakhstan. The share of rural detached houses using solid fuels was very high in regions without gas pipelines: East Kazakhstan (99%), North Kazakhstan (99%), Pavlodar (99%), Akmola (98%) and Karaganda (95%). Regions with a gas pipeline network (mainly in western Kazakhstan) have substantially lower solid fuel use in rural detached houses: Mangistau (0%), West Kazakhstan (1%), Atyrau (4%), Aktobe (29%) and Zhambyl (37%).
In 4 regions out of 14, however, solid fuel use remains high among detached rural households despite access to pipeline natural gas: Kyzylorda (95%), Almaty (81%), South Kazakhstan (57%) and Kostanay (80%). In these regions, households continue to rely on coal – possibly because of the high cost of connecting to the pipeline, the expense of a gas boiler, the relatively higher price of gas, distribution network unavailability, and/or income poverty. Specific support programmes (e.g. subsidies) to help households switch from coal to gas are not yet in place.
Low population density is one of the limiting factors for gas pipeline development. In 2018, Kazakhstan’s average population density in was 6.8 people per square kilometre (/km2), varying by region from 2.9/km2 to 17.4/km2 (Bureau of National Statistics, Agency for Strategic Planning and Reforms, 2020).
Regions in Central Kazakhstan (Nur-Sultan city and the Karaganda and Akmola regions) that currently rely heavily on coal are expected to gradually switch to gas in upcoming years, owing to completion of the Saryarka gas pipeline in 2019 and ongoing extension of the gas distribution network.
Share Of Kazakhstan Urban Apartment Households Using Solid Fuels
Open
Share Of Kazakhstan Urban Detached Households Using Solid Fuels
Open
Share Of Kazakhstan Rural Apartment Households Using Solid Fuels
Open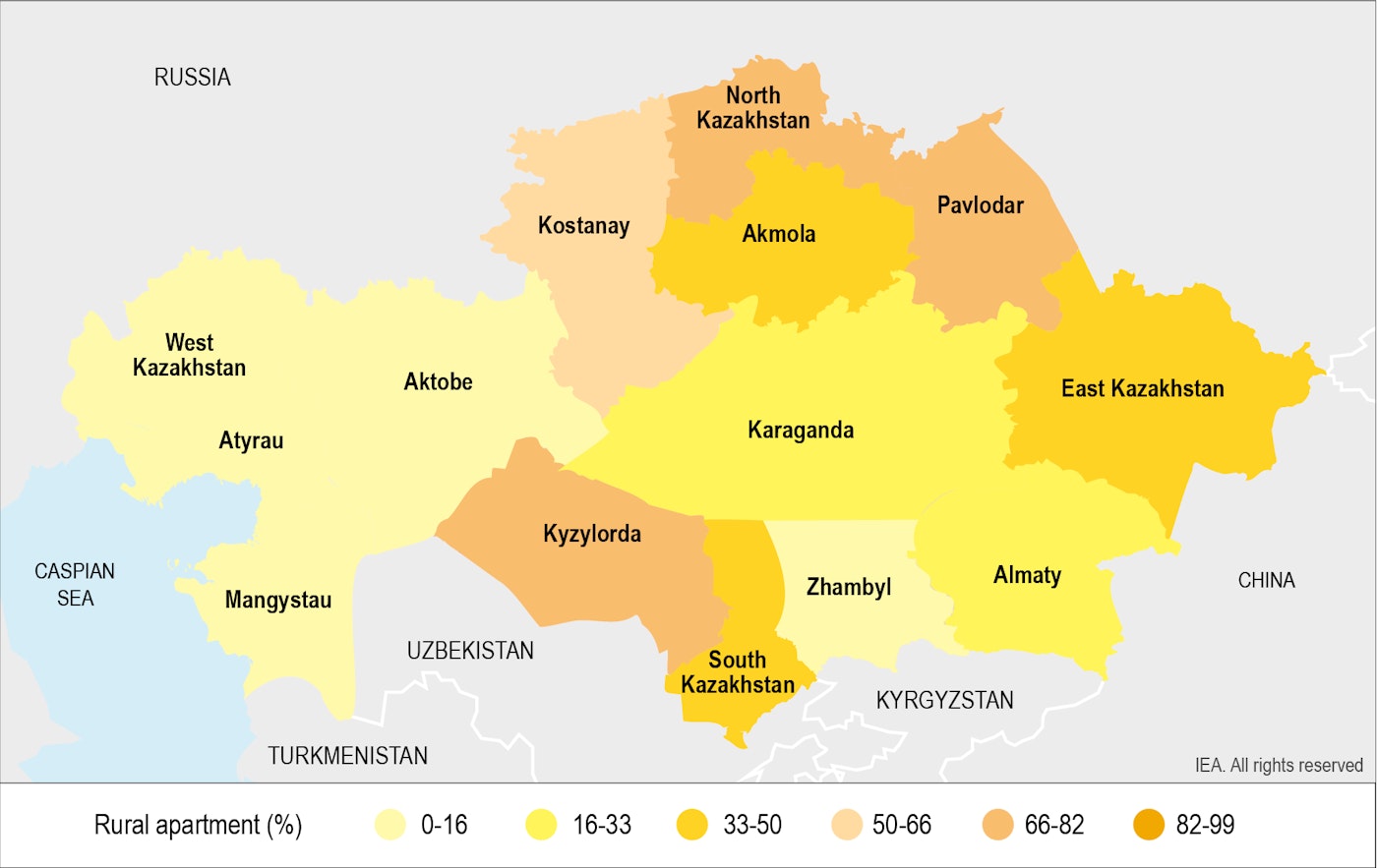
Share Of Kazakhstan Rural Detached Households Using Solid Fuels
Open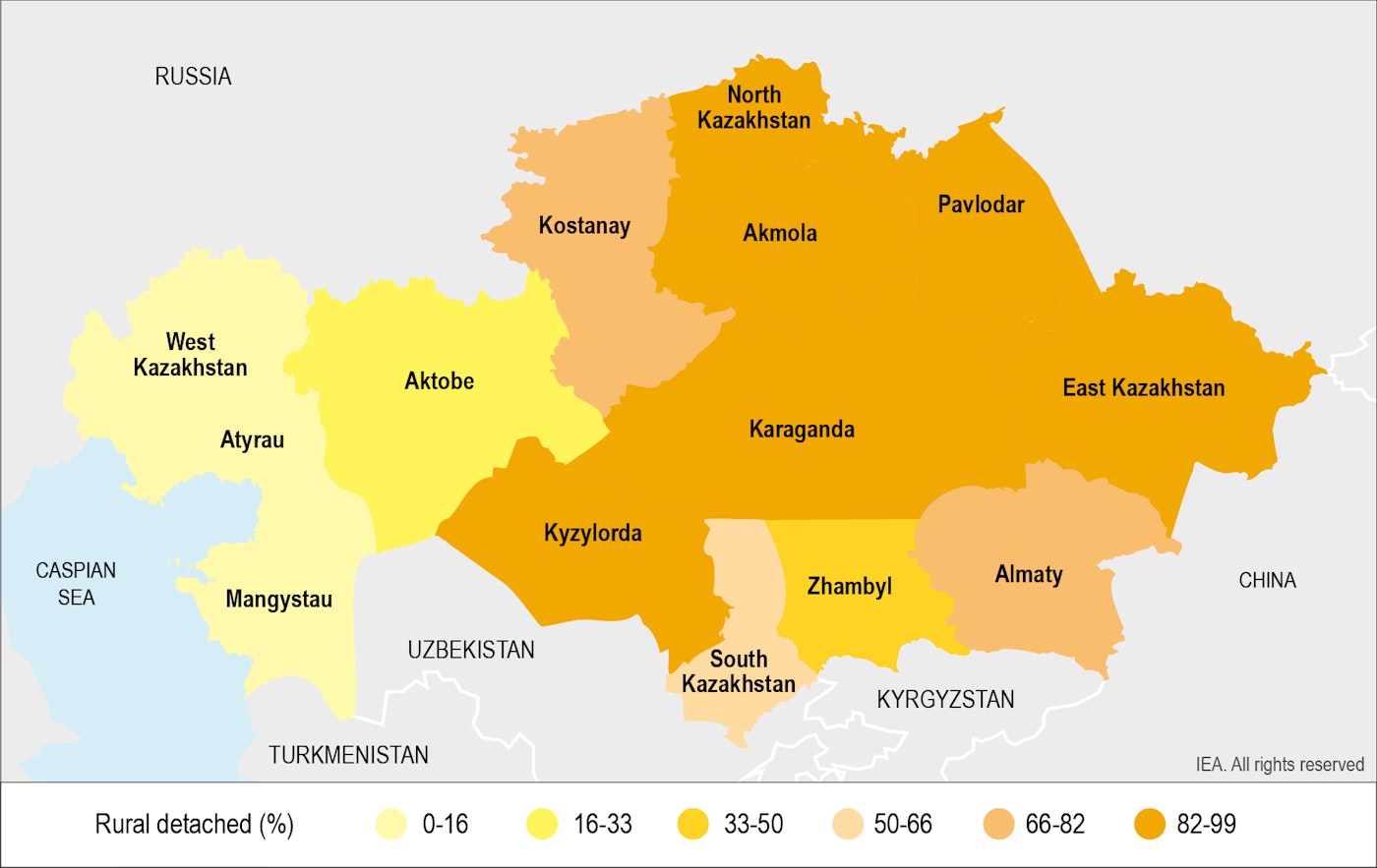
Most households tend to use several types of fuel during the year rather than just one. Only 7% of households using solid fuels relied exclusively on coal in 2018, whereas 51% used a combination of coal, firewood and propane, and 30% used coal and propane. Propane (when used with coal) was used for cooking in 93% of households. Firewood alone was used by only 1% of households; it was used mainly in combination with coal and propane.
Kazakhstan households using solid fuels, by fuel combination
OpenThe use of solid fuels was diverse in 2018: 43% of households used coal for heating and cooking; 36% used it for heating; and 18% for heating, water heating and cooking. Concerning firewood, 40% of households used it for heating; 31% for heating and cooking; and 15% for heating, water heating and cooking.
Kazakhstan household coal consumption, by end use
OpenStove designs, operation times, fuel heating values, fuel characteristics and emissions rates can vary significantly from one household to another. There are currently no studies that quantify indoor air pollution in Kazakh households or the efficiencies of their heating devices, nor were studies found for other post-soviet countries with potentially similar heating devices and emissions rates. While wealthier urban households may have modern boilers (water-based heating), poorer ones may have to rely on hand-made brick stoves (heating based on air radiation).

Kazakhstan Solid Fuel Stoves
Average daily coal consumption per household was analysed based on data from the household survey.1 This indicator varied significantly – from 6 kilogrammes (kg) to 46 kg (the number of heating days in a year ranges from 143 to 222, depending on the region). Some regions with a gas network (and a warmer climate) had lower daily coal consumption: Almaty (16 kg), West Kazakhstan (15-17 kg) and Aktobe (21-24 kg). However, some warmer regions (with a gas network) had relatively high average daily coal consumption: Zhambyl (35 kg) and South Kazakhstan (39-46 kg). Thus, although most regions are in line with average daily coal consumption in the Hebei Province of the People’s Republic of China (hereafter, “China”) (25-30 kg) (Zhao et al., 2018), Kazakhstan’s national average consumption per day was 31 kg in urban areas and 33 kg in rural areas. Unsurprisingly, rural coal consumption is generally higher than urban use.
Average daily coal consumption per surveyed household by surface area
| Coal consumption (t) | t/house/yr | kg/m2 | kg/day/house | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | |||
| Akmola region | 2 151 | 1 663 | 5.8 | 5.9 | 87 | 77 | 27 | 27 | ||
| Aktobe region | 206 | 223 | 4.2 | 4.9 | 67 | 60 | 21 | 24 | ||
| Almaty region | 3 225 | 2 997 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 78 | 66 | 28 | 28 | ||
| Atyrau | 0 | 25 | 5.0 | 54 | ||||||
| West Kazakhstan region | 14 | 3 | 3.4 | 3.0 | 51 | 36 | 17 | 15 | ||
| Zhambyl region | 306 | 985 | 5.8 | 5.8 | 82 | 71 | 35 | 35 | ||
| Karaganda region | 2 179 | 1 476 | 6.8 | 6.7 | 91 | 88 | 32 | 31 | ||
| Kostanay region | 200 | 2 129 | 4.2 | 6.2 | 73 | 93 | 19 | 29 | ||
| Kyzylorda region | 100 | 1 422 | 4.5 | 4.8 | 49 | 45 | 27 | 28 | ||
| Mangistau region | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| South Kazakhstan | 1 325 | 3 927 | 5.6 | 6.5 | 64 | 64 | 39 | 46 | ||
| Pavlodar region | 367 | 1 706 | 5.7 | 6.1 | 92 | 86 | 27 | 29 | ||
| North Kazakhstan region | 407 | 1 697 | 4.5 | 5.1 | 70 | 69 | 20 | 23 | ||
| East Kazakhstan region | 1 360 | 3 154 | 4.3 | 5.1 | 80 | 85 | 21 | 25 | ||
| Nur-Sultan | 92 | 0 | 1.3 | 13 | 6 | |||||
| Almaty | 71 | 0 | 2.7 | 34 | 16 | |||||
| Total | 12 001 | 21 405 | 5.2 | 5.6 | 76 | 72 | 31 | 33 | ||
Source: Adapted from the Households Survey on Fuel and Energy Consumption (Bureau of National Statistics, Agency for Strategic Planning and Reforms, 2018).
The correlation between average coal consumption and duration of the region’s heating season was perhaps less strong than anticipated. The general trend is for daily coal consumption to be higher in regions with shorter heating periods, which could result from greater stove and building efficiency in the colder regions. Households in colder climates may also try to save their coal.
Natural gas use by Kazakh households
Use of natural gas by households is dependent on the availability of natural gas network and price. Out of 21 000 surveyed households, 41% were using natural gas (for all purposes, including for heating, water heating and cooking purposes). The share of natural users by house type was as follows: 45% of urban apartments, 50% of urban detached houses, 31% of rural apartments and 31% of rural detached houses. Majority of the households in the western regions of Kazakhstan rely on natural gas due to the developed gas pipeline infrastructure and low gas prices. There is a main gas pipeline available in the southern regions of Kazakhstan, but share of gas is relatively low in rural areas due to relatively high cost of connection, higher prices of gas and lack of distribution pipelines. Regions in the north, center and east of Kazakhstan do not use natural gas (except for Kostanay region) due to unavailibility of natural gas pipeline and gas supplies.
References
Likely reporting errors were identified (i.e. households reporting unrealistically high fuel consumption) and excluded from the analysis of fuel consumption. Therefore, households using more than 10 t of coal (310 households) were omitted from the analysis.
Reference 1
Likely reporting errors were identified (i.e. households reporting unrealistically high fuel consumption) and excluded from the analysis of fuel consumption. Therefore, households using more than 10 t of coal (310 households) were omitted from the analysis.